Your Poop Schedule Says a Lot About Your Overall Health, Study Finds
A study published in Cell Reports Medicine reveals that bowel movement frequency significantly influences physiology and long-term health, with the best outcomes linked with passing stools once or twice a day.
Previous research has suggested associations between constipation and diarrhea with higher risks of infections and neurodegenerative conditions, respectively.
But since these findings were observed in sick patients, it remained unclear whether irregular bathroom visits were the cause or result of their conditions.
“I do hope that this work will kind of open clinicians’ minds a bit to the potential risks of not managing bowel movement frequencies,” senior author Sean Gibbons at the Institute for Systems Biology told AFP, explaining that doctors often view irregular movements as merely a “nuisance.”
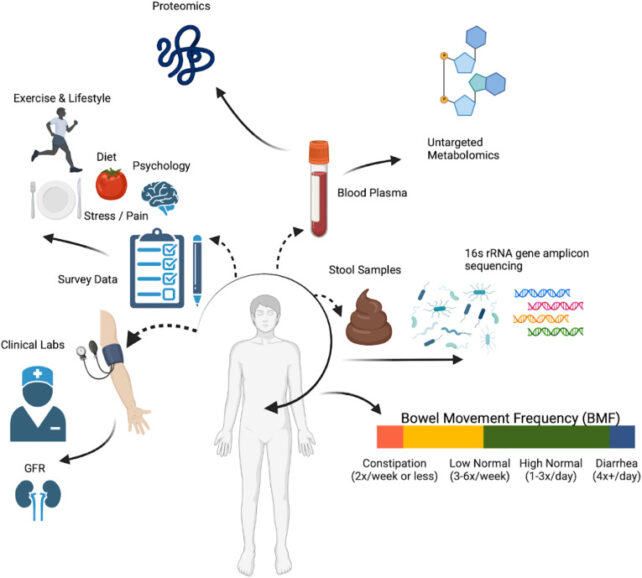
Gibbons and his team collected clinical, lifestyle, and biological data – including blood chemistry, gut microbiome, genetics and more – from over 1,400 healthy adult volunteers with no signs of active disease.
Participants’ self-reported bowel movement frequencies were categorized into four groups: constipation (one or two bowel movements per week), low-normal (three to six per week), high-normal (one to three per day), and diarrhea.
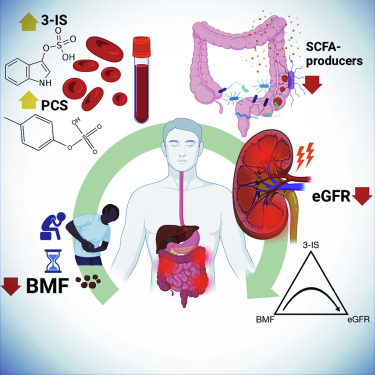
When stools linger too long in the gut, microbes exhaust the available fiber – which they ferment into beneficial short-chain fatty acids – and instead ferment proteins, producing toxins like p-cresol sulfate and indoxyl sulfate.
“What we found is that even in healthy people who are constipated, there is a rise in these toxins in the bloodstream,” said Gibbons, noting that these toxins are particularly burdensome to the kidneys.
Fruits and vegetables key
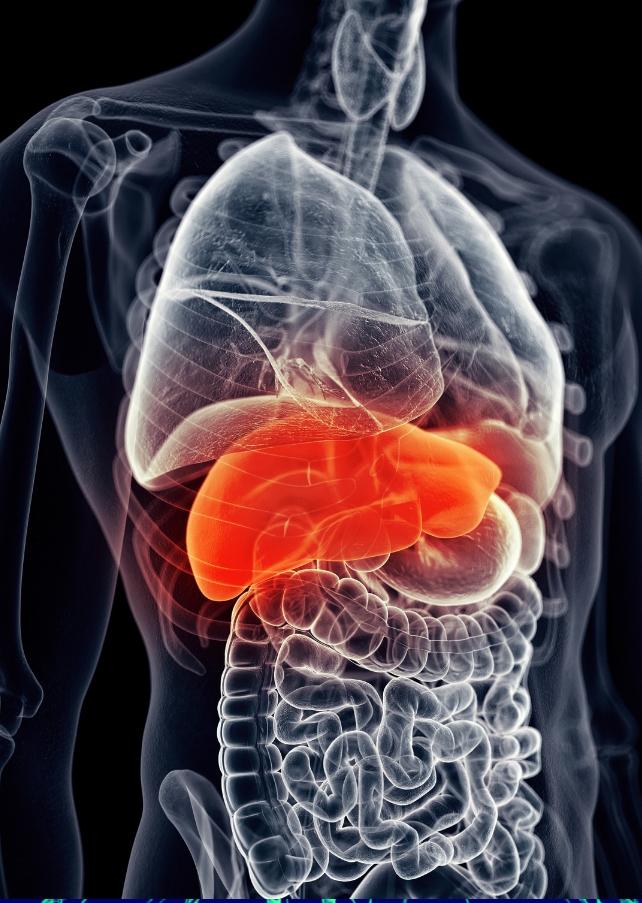
In cases of diarrhea, the team found clinical chemistries indicative of inflammation and liver damage.
Gibbons explained that during diarrhea, the body excretes excessive bile acid, which the liver would otherwise recycle to dissolve and absorb dietary fats.
Fiber-fermenting gut bacteria known as “strict anaerobes,” associated with good health thrived in the “Goldilocks zone” of one or two poops a day.
However, Gibbons emphasized that more research is needed to define this optimal range more precisely.
Demographically, younger people, women, and those with a lower body mass index tended to have less frequent bowel movements.
Hormonal and neurological differences between men and women may explain the gap, Gibbons said, along with the fact that men generally consume more food.

Finally, by pairing biological data with lifestyle questionnaires, the team painted a clear picture of those who typically fall into the Goldilocks Zone.
“It was eating more fruit and vegetables, that was the biggest signal we saw,” said Gibbons, along with drinking plenty of water, regular physical activity, and eating a more plant-dominant diet.
The next step in the research could involve designing a clinical trial to manage the bowel movements of a large group of people, followed over an extended period to assess its potential in disease prevention.
